MLZ ist eine Kooperation aus:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ ist Mitglied in:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ in den sozialen Medien:

MLZ
Lichtenbergstr.1
85748 Garching
Advanced Materials Group
The development of advanced materials is influenced strongly by the use of various material characterization methods. Investigations of crystallographic structures, phase transformations, particle morphologies and sizes, defect characterizations are key aspects. The Advanced Materials Group utilizes various neutron techniques (occasionally positron techniques generated by neutrons at the MLZ) to study central questions in the field of energy related topics as batteries and high-temperature alloys.
Batteries
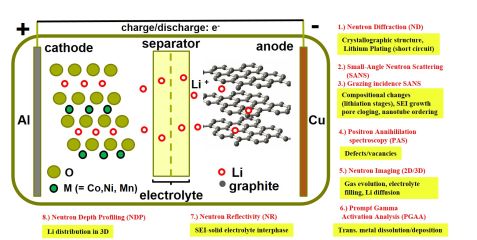
Battery research using neutrons and positrons (R. Gilles, J. Synch. Investig.: X-ray, Synch. and Neutron Techn. 14, S69–S74 (2020)).
In the field of batteries, a huge demand emerged to follow electrochemical processes in situ or operando to understand in detail the mechanisms of energy storage systems. Neutrons were identified as a highly suitable probe thanks to their special properties, such as large penetration depths in materials, the non-destructive interaction due to meV energy transfer, the high sensitivity for light elements as especially Li and H in the presence of heavy elements and the easy distinction of neighbor elements or various isotopes of a single element.
Besides the well-established method of neutron diffraction using the LiCx peaks to study the intercalation or de-intercalation of Li in the graphite anode, other techniques became available to study other phenomena in battery research. Using the imaging techniques, the visualization of electrolyte filling, gassing or the Na liquid level of a ZEBRA cell in operation could be examined. Small-angle neutron scattering with the method of scattering-contrast variation (protonated and deuterated labelled samples to vary the sensitivity for example of the electrolyte) open another kind of application to receive further information on shell structures of electrode materials. Further techniques as neutron reflectivity, grazing incidence small-angle neutron scattering, positron annihilation spectroscopy using neutrons converted into positrons or prompt gamma activation analysis have been successful used. The available technologies at MLZ offer in situ cell diagnostics and ensure comprehensive process conclusions from combining application based research results with fundamental research. This opens up development potentials in many battery research fields like cost reduction, simplification of production processes, performance and aging of batteries.
High-Temperature Alloys
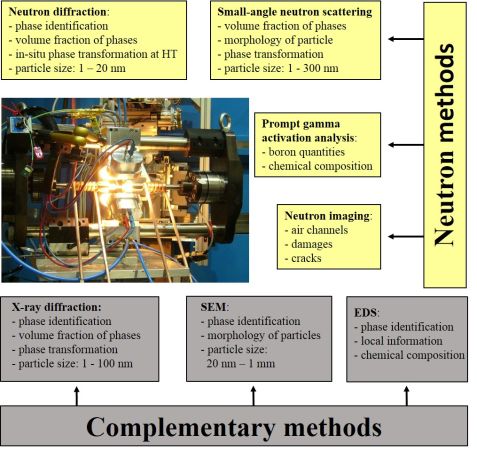
Neutron and complementary methods for the investigation of high-temperature alloys (R. Gilles, J. Synch. Investig.: X-ray, Synch. and Neutron Techn. 14, S69–S74 (2020)).
High-temperature alloys play a very important role in the strategy of sustainable energy resources. Their typical application fields are engine jets, stationary gas turbines and oil and gas transportation tubes. In addition, high-temperature alloys are used for hot-working tools, fans and furnace mufflers, heat exchangers, turbochargers, exhaust valves, rocket propulsions and medical components (dentistry and prostheses).
The low absorption of neutrons by a majority of materials enable neutron scattering techniques suitable for bulk characterization as well as for in-situ studies at operation conditions (e.g. high temperatures). By neutron diffraction it is possible to determine the phases present in the alloy as well as their volume fractions. With in situ investigations it is possible to determine solvus temperatures of the different phases, to follow the cell parameters evolution with temperature and to study changes in the mechanical response of the different phases under tensile/compressive tests. Small-angle neutron scattering provides information on the microstructures, i.e. morphology, sizes and volume fraction of the nanosized precipitates and by in situ studies it is possible to study the evolution of the precipitates with temperature and under tensile/compressive tests. In parallel a new testing machine that allows tension and compression of up to 100 kN with heating up to 1200 °C is set up to allow under development in order to allow in situ ND and SANS tests under tension and compression and temperature that will provide information about the structural-mechanical properties correlation of the studied materials and even simulate the forging process. Further applications as neutron depth profiling for boron distribution or neutron imaging of complete turbine discs or defect studies on alloys with positrons etc. enables to extend the studies with neutrons in this field.
Applied methods of the Advanced Materials Group
- Neutron diffraction (ND) The method of neutron diffraction allows to gather information on the chemical composition as well as the structure of the involved phases and their changes during electrochemical processes, temperature and mechanical tests. With these one can reveal e.g. loss of active lithium during aging, observes Li-plating or determine solvus temperature of constituting phases of a alloy.
- Neutron imaging (NI) With imaging methods like radiography (2D) or tomography (3D) visualization of structures inside of a batteries as the distribution of electrolyte or Li during filling or cycling of cells. Cooling channels of turbine plates or other inhomogeneities in submillimeter range of alloys are visible.
- Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS, resp. GISANS) With the methods of small-angle neutron scattering in transmission (SANS) or in reflection geometry (GISANS) information on size, shape and volume fractions of nano structures can be obtained during aging processes resp. during charging and discharging of batteries or during heating (grains coarsening and phase dissolution) or cooling down (phases precipitation) in superalloys.
- Neutron depth profiling (NDP) The method of neutron depth profiling allows to determine concentration profiles near the surface of certain isotopes, like 6Li, N, S or B.
- Prompt gamma activation analysis (PGAA) allows to determine element (resp. isotope) composition of a sample. The analysis allows often the determination even of small contaminations of electrodes (typically down to the ppm-level or even below). In alloys the boron addition on ppm level can be identified.
- Positron annihilation spectroscopy (PAS) At the FRM II the most intense positron beam in the world is created by the use of neutrons. The unique property of positron radiation is its sensitivity to the presence of perturbations in the crystal lattice. These defects change the energy distribution as well as the life time of the annihilation radiation and allows to draw conclusions on the type and amount of defects in electrode materials correlated to ageing behaviour. Defect characterization in alloys allows to understand order and disorder phenomena in alloys.
- Classical analytical methods like x-ray diffraction (XRD) as well as small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) are also complementarily available at MLZ in the Materials Science Lab of the group. Different wavelengths or a tempered (-30 to +60 °C) sample chamber for operando studies of thin pouch bag cells with XRD are available. Pouch cells in transmission mode and bulk alloys in Bragg Brentano geometry are typical applications for sample characterization.
- Quasi-elastic neutron scatteirng (QENS) With this method the diffusion of hydrogen or sodium can be studied with high precesion of jumping lengths and time resolution up to pico seconds. Heating experiments allow to determine the activation energy of the involved charge particles.
Selected Publications
Head of the group
Dr. habil. Ralph Gilles
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14665
E-Mail: ralph.gilles@frm2.tum.de
Lithium ion batteries:
Thien An Pham
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-11774
E-Mail: thienan.pham@frm2.tum.de
Ivana Pivarnikova
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-54819
E-Mail: ivana.pivarnikova@frm2.tum.de
Dr. Seda Ulusoy
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-11656
E-Mail: seda.ulusoy@frm2.tum.de
Advanced alloys:
Dr. Massimo Fritton
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-54826
E-Mail: massimo.fritton@frm2.tum.de
Alexander Mutschke
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-54827
E-Mail: alexander.mutschke@frm2.tum.de
Simon Sebold
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14641
E-Mail: simon.sebold@frm2.tum.de
Dr. Stefan Engel
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-54819
E-Mail: stefan.engel@frm2.tum.de
Links
Current Projects:
- BMBF: AlaAF
- BMBF: H2MaT
- BMBF: LiSI-2
- BMBF: TUBE
- BMWi: CAESAR
Former Projects:
- BMBF: INA780
- BMBF: HiMat
- BMBF: LiSI
- BMBF: ExZellTUM
- BMBF: ExZellTUM II
- BMBF: ExZellTUM III
- BMBF: 4D N4DP
- BMBF: Time resolved N4DP
- BMBF: CharLiSiKo
- Bayerische Staatsregierung: EEBatt
- DFG: CoRe alloys
- DAAD: CSC High-temperature alloys
- DAAD: CoRe alloys
MLZ ist eine Kooperation aus:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ ist Mitglied in:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ in den sozialen Medien:



