MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media:

MLZ (eng)
Lichtenbergstr.1
85748 Garching
STRESS-SPEC
Materials science diffractometer
In response to the development of new materials and the application of materials and components in new technologies, the direct measurement, calculation, and evaluation of textures and residual stresses has gained worldwide significance in recent years.
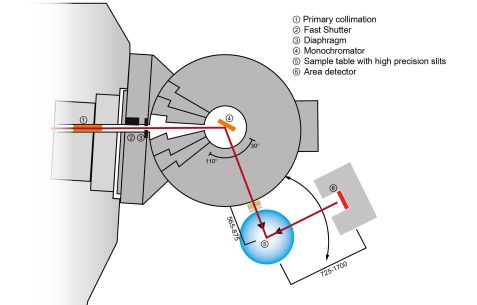
STRESS-SPEC, the materials science diffractometer, is located at the thermal beam tube SR-3 and can easily be configured either for texture analysis or strain measurements.
The set-up utilises three different monochromators: Ge(511), bent silicon Si(400), and pyrolitic graphite PG(002). This selection of monochromators and the possibility to automatically vary the take-off angles from 2θM = 35º to 110º allows us to find a good compromise between resolution and intensity for each measuring problem.
The gauge volume defining optical system of primary and secondary slits is designed with regard to the reproducibility of geometrical alignment and sturdiness. Instead of the slits, a set of radial collimators is available to define the gauge volume.
Samples can be aligned using theodolites and a camera system. In addition, the possibility of scanning surfaces of components offline using a CMM scanner is available.
- Industrial components
- Welds, additive manufactured samples
- Superalloys
- Strain mapping
- Surface measurements from 150 µm possible [2]
- Global textures
- Local textures
- Strain pole figures
- FHWM pole figures
- Phase transformation dynamics
- Spatially resolved phase analysis (e.g. batteries)
[1] Hofmann, M. et al., Physica B 385, 1035 (2006).
[2] Saroun, J. et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 46, 628 (2013).
[3] Brokmeier, H.-G. et al., NIM-A 642, 87 (2011).
- xyz-table
- Capacity 300 kg, travel xy = ±120 mm, z = 300 mm, accuracy ~ 10 µm
- Load frame
- +/-50 kN, heatable to 1000°C (in air), rotabale
- +/-100 kN, heatable to 1500°C (vacuum)
- Full circle Eulerian cradle (max. load 5 kg)
- ¼ circle Eulerian cradle for heavy samples
- Standard sample environment (e.g. furnace, cryostat)
- Quenching & deformation dilatometer
A positioning system consisting of a Stäubli 6-axes robotic arm for texture and strain measurements (payload up to 30 kg) can be mounted instead of the standard sample table. It offers more flexibility than an Eulerian cradle and can also be used as an automatic sample changer for texture measurements [4]. A camera-based metrology system tracks the sample position [5].
[4] Randau, C. et al., NIM-A 794, 67 (2015).
[5] Landesberger et al., Sensors 24(9), 2703 (2024).
- Beam tube SR-3
- Thermal neutrons
- Collimators (‘in-pile’) 15’, 25’, open
- Ge(511), Si(400), PG(002)
- 2θM 35° – 110° continuous
- Wavelength 1 Å – 2.4 Å; (2.5 Å-1 < Q < 10.5 Å-1)
- Primary slit: automatically continuously variable up to 7 × 17 mm2 (W x H)
- Secondary slit: continuously variable up to 15 mm
- Radial collimators – incoming beam (FOV = 1 mm, 2 mm, 5 mm)
- Radial collimators – diffracted beam (FOV = 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm, 5 mm, 10 mm)
- Primary slit: max. 30 × 40 mm2 (W x H)
- Secondary slit: continuously variable up to 15 mm or open
- 3He-PSD, 25 × 25 cm2; 256 × 256 pixels
STeCa2 [6]
STeCa2 is the standard software tool for analysing the 2D-detector data of STRESS-SPEC. Besides display functionalities, various functions for integration and Bragg peak refinement are available. In addition, one can generate and visualise the pole figures from texture measurements. The software is available for Linux or Windows and can be downloaded from the web page of the Computing Group
DISEMM (Diffraction assisted mechanical modelling) [7]
The software DISEMM is designed to analyse diffraction data from in-situ loading experiments to obtain diffraction elastic and single-crystal elastic constants and to describe the mechanical behaviour by the elasto-plastic self-consistent modelling. DISEMM offers a variety of grain-to-grain interaction models and integrates texture and multi-phase alloys. The software is currently available for Windows. The DISEMM software can be downloaded here, with the corresponding manual here.
STRESSFIT [8, 9]
is a Python package for fitting neutron residual strain scanning data. The primary objective is to restore intrinsic lattice strain distributions measured by neutron diffraction. In an experiment, this distribution is smeared by the finite spatial resolution of the instrument. Measured strains are also affected by so-called pseudo-strains, which generally arise from an inhomogeneous sampling of the material. The best known is the surface effect, which occurs when the nominal gauge volume of the instrument is only partly immersed under the sample surface. This gives rise to peak shifts (pseudo strains) of similar magnitude as the intrinsic strain. The Python package can be reached here (https://github.com/NPLtools/stressfit), as well as the respective available documentation.
[6] Randau, C. et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 641 (2011).
[7] Heldmann, A. et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 52, 1144 (2019).
[8] Rebelo Kornmeier, J. et al. Materials Characterization, 154, 53 (2019).
[9] Šaroun, J. et al., Physica B: Condensed Matter 551, 468 (2018).
Instrument scientists
Dr. Michael Hofmann
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14744
E-mail: michael.hofmann@frm2.tum.de
Dr. Weimin Gan
Phone: +49 (0)89 158860-766
E-mail: weimin.gan@hzg.de
STRESS-SPEC
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14814
Operated by


Funding


News
Publications
Find the latest publications regarding STRESS-SPEC in our publication database iMPULSE:
Citation templates for users
In all publications based on experiments on this instrument, you must provide some acknowledgements. To make your work easier, we have prepared all the necessary templates for you on this page.
Instrument control
Gallery




MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media: