MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media:

MLZ (eng)
Lichtenbergstr.1
85748 Garching
POLI
Polarised hot neutron diffractometer
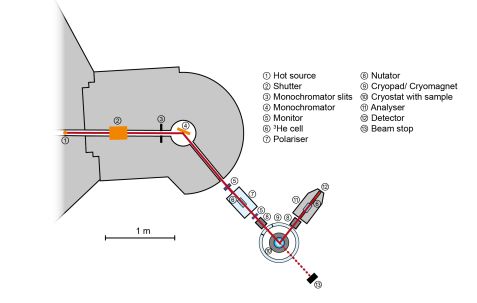
POLI is a versatile two axes single crystal diffractometer mostly dedicated to investigating magnetic structures in single crystals using neutron spin polarisation. The instrument is equipped with two non-polarising variably focussing monochromators, which can be combined with optimised polarisers to allow structural investigations using polarised and non-polarised neutrons with short wavelengths and high resolution.
Three standard set-ups are currently implemented on POLI:- Zero-field spherical neutron polarimetry (SNP) using third-generation CRYOPAD
- Polarised neutron diffraction (PND) in the magnetic field known as Flipping-Ratio method
- Non-polarised diffraction under special conditions (very low temperatures, magnetic and electric fields, high pressures, high temperatures and their combinations) using dedicated sample environments and out-of-plane lifting counter
Also, non-standard set-ups, e.g. for high-field polarisation analysis, resonant fission experiments in heavy nuclei, irradiation or other applications, are possible on request.
The SNP method allows us precisely determine the change in the direction and value of the neutron polarisation during the scattering process in the sample by measuring the nine components of the so-called polarisation matrix for an individual Bragg reflection. The observed change in the neutron polarisation gives access to the 16 independent correlation functions involved in the most general nuclear and magnetic scattering processes and, thus, allows to determine the direction of the magnetic interaction vector of even complex magnetic structures. For those structures with nuclear and magnetic reflections coinciding in the reciprocal space, the amplitude of the magnetic interaction vectors, and hence the magnetisation distribution, can additionally be determined from SNP. Moreover, the technique can be employed to study magnetic domain distributions. For SNP, polarised 3He spin filters are used as polarisers and analysers, as they offer the best performance for hot neutrons. By tuning the pressure of 3He in the filter cell, they can be optimised for the used wavelength or the experimental needs. An automatic correction for the time-dependent neutron polarisation is applied. An upgrade from the 3He MEOP to an in-situ polarising SEOP system is currently ongoing.
The PND method is another powerful tool for the investigation of magnetic structures. With the sample situated in strong magnetic fields and a polarised incoming neutron beam, two scattering cross-sections are measured for each Bragg reflection for the two polarisation directions parallel and antiparallel to the magnetic field, and the asymmetry between them is built. Compared to the non-polarised neutron diffraction, this asymmetry gives additional access to contributions from the magnetic chirality and the interference between the nuclear and magnetic scattering. This interference term is especially powerful as it depends linearly, and not quadratic, on the magnetic structure factor, which increases the precision in the determination of small ordered magnetic moments by at least one order of magnitude and provides unique access to phase information. Depending on the experimental needs, a 3He spin filter cell or a dedicated supermirror bender is used as a polariser. An upgrade from the out-of-plane lifting counter detector to a small 2D PSD detector is currently ongoing.
- Complex commensurate and incommensurate magnetic structures studied in the ground state (zero-field), which is especially useful for superconductors
- Studies of magnetic and magneto-electric domains using SNP on samples cooled in zero-field as well as in external magnetic or electric fields.
- Mapping out of the magnetic phase diagrams by field, temperature, pressure etc.
- Studies on multiferroic materials by simultaneous application of magnetic and electric fields
- Determination of magnetic form factors, magnetisation density distribution maps, local susceptibility tensors (also in certain antiferromagnets).
- Absolute sign determination of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction vector in e.g. weak ferromagnets or chiral structures
- Crystal structure determination under special conditions
- Search for the T-odd violation in the fission reactions of the heavy nuclei
- Standard closed-cycle cryostat (CCR): 3.7 – 425 K
- Variox LHe cryostat: 1.5 – 300 K
- Lower temperature inserts for CCR or Variox on request:
- 3He: 0.45 – 4 K
- 3He/4He dilution: 0.05 – 1 K
- 2.2 T HTS magnet in combination with standard CCR and/or low-temperature insert
- 8 T dedicated magnet (1.7 – 800 K); in combination with Kelvinox dilution insert (0.05 K) on request
- Electric field up to 10 kV
- High pressure cells on request
- Beam tube SR-9a on hot source
| Crystal | λ | Flux | λ | Flux |
| Å | n cm-2 s-1 | Å | n cm-2 s-1 | |
| Cu (220) | 0.55 | 5,5 × 106 | 0.9 | 1.4 × 107 |
| Si (311) | 0.7 | 7 × 106 | 1.15 | 1.8 × 107 |
- Er filter for suppression of λ/2- or λ/3-contamination of the monochromatised beam
- 3He MEOP spin filter cell:
- Diameter: 60 mm, length: 130, 160 mm
- Neutron polarisation: 0.8 – 0.93
- Neutron transmission: 0.2 – 0.27
- Cell holding time: 2 days
- Cells replacement time: 10 min
- To be commissioned in 2025: 3He SEOP in situ polariser:
- Diameter: 70 mm, length: 150 mm
- Neutron polarisation: 0.93 – 0.98
- Neutron transmission: 0.22 – 0.28
- Supermirror bender polariser:
- Fe/Si m = 3 supermirror
- Beam cross-section H x W: 130 × 42 mm2
- Neutron polarisation: > 0.99
- Total transmission: 0.07 – 0.09
| Non-polarised | PND (8 T magnet) | SNP (Cryopad) |
| -20° < 2θ < 130° | -20° < 2θ < 130° | -15° < 2θ < 120° |
| -180° < ω < 180° | -180° < ω < 180° | -180° < ω < 180° |
| -5° < ξ1 < 5° | -4° <ξ1 = 0° | -4° < ξ1 < 4° |
| -5° < ξ2 < 5° | -4° < ξ2 = 0° | -4° < ξ2 < 4° |
| -4.2° < v < 30° | -4.2° < v < 25° | v = 0° |
- Precision in polarisation control: better 1°
- Low background / low absorption
- LHe autonomy: 10 days
- LN2 refill (automatic): daily
- Space for closed cycle cryostat or orange type cryostat
- 2” end window 3He single counter tube optimised for hot neutrons
- Small 2D PSD with 1 – 2 mm resolution (under development 2025)
Instrument scientists
Dr. Leonie (Heinze) Stödter
Phone: +49 (0)89 158860-811
E-mail: l.stoedter@fz-juelich.de
POLI
Phone: +49 (0)89 158860-518
Operated by


Funding

News
Publications
Find the latest publications regarding POLI in our publication database iMPULSE:
Citation templates for users
In all publications based on experiments on this instrument, you must provide some acknowledgements. To make your work easier, we have prepared all the necessary templates for you on this page.
Instrument control
Gallery

MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media: